Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and portable devices, come equipped with various safety mechanisms to ensure their stable and safe operation. One of these crucial safety features is the vent valve, also known as the VENT. This valve serves a vital role in preventing dangerous conditions that could arise from the build-up of gases inside the battery due to overcharging, overheating, or other failures. The vent valve is specifically designed to release excess internal pressure, ensuring that the battery does not swell, leak, or potentially explode.
The Working Principle of the Vent Valve
The primary function of the vent valve is to maintain the safety and integrity of the battery by controlling internal pressure. When a lithium battery experiences abnormal conditions, such as overcharging, a short circuit, or excessive heating, gases like hydrogen or oxygen may be produced inside the battery. If the pressure inside the battery becomes too high, it could result in swelling, leakage, or even rupture. In such cases, the vent valve automatically opens to release the gas, thereby alleviating the pressure buildup and preventing potential hazards.
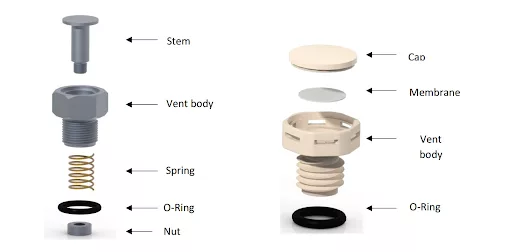
The vent valve mechanism is generally a physical valve that activates based on changes in pressure. It does not rely on sensors or electronic signals, but instead operates by detecting when the internal pressure exceeds a predetermined threshold. Once the critical pressure point is reached, the valve opens and allows the excess gas to escape, ensuring the safety of the battery.

Comparing the Vent Valve to Other Safety Mechanisms: The Airbag System
A helpful comparison to better understand the vent valve’s role is the airbag deployment mechanism found in vehicles. Both the airbag system and the lithium battery vent valve are designed to protect against harm in the event of an unexpected or abnormal situation—such as a collision for airbags and an overcharge or overheating for batteries.
In the case of airbags, sensors detect the severity of a collision and trigger the rapid inflation of the airbag to cushion the impact. Similarly, the lithium battery vent valve releases gas when internal pressure reaches unsafe levels, preventing a potentially dangerous situation. While both systems rely on real-time detection of hazardous conditions, the vent valve’s role is specifically focused on managing pressure to prevent battery rupture or explosion, while airbags protect occupants from injury during a crash.
Does the Vent Valve Affect Waterproofing?
One concern that arises with the incorporation of vent valves in lithium batteries is their impact on the waterproofing effectiveness of the battery pack. This concern is particularly relevant for batteries used in electric vehicles or portable devices that may be exposed to water or harsh environmental conditions.
Fortunately, modern lithium battery designs, such as those used in products like electric vehicles, are specifically engineered to address this issue. Many vent valves, like those used in the Olelon vent valve, undergo rigorous testing to ensure their performance under waterproofing standards. For instance, Olelon’s vent valve design has been tested to meet IP67 standards, which ensures that the battery pack remains sealed against water ingress under normal conditions.
In typical usage, the vent valve remains closed, effectively maintaining the waterproof integrity of the battery. When the battery is not in use, the vent valve is sealed with a cap, further preventing water from entering. The valve only opens in specific situations—when the internal pressure of the battery reaches a critical level due to heating or gas generation. Once this threshold is surpassed, the valve opens to release gas, balancing the pressure between the inside and outside of the battery.
It is important to note that, although the vent valve opens in certain conditions, it is designed to do so only when necessary to ensure the safety of the battery. The valve remains sealed and maintains the waterproof effectiveness of the battery under normal conditions, preventing any water from entering the battery pack during routine use. This makes sure that the vent valve does not compromise the overall waterproofing capabilities of the battery.
Conclusion
In summary, the vent valve in a lithium-ion battery plays a crucial role in maintaining battery safety by releasing excess pressure when needed. It functions as a physical valve that opens automatically to vent gases produced under abnormal conditions like overcharging or overheating. While there may be concerns about waterproofing, modern designs, such as those tested to IP67 standards, ensure that the vent valve only opens when required, without compromising the integrity of the battery pack. As a result, the vent valve contributes to both the safety and longevity of the battery, allowing it to perform reliably even in demanding environments.

