1. Definition
Nominal Voltage
Nominal voltage refers to the average operating voltage of a battery under normal conditions. It is a standardized reference value that helps users understand a battery’s expected performance during operation. This value is neither the maximum nor the minimum voltage but represents an approximate midpoint of the battery’s discharge curve.
Different battery chemistries have distinct nominal voltages:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries: 3.2V per cell
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries: 3.7V per cell
For battery packs, the nominal voltage is calculated by multiplying the nominal voltage of a single cell by the number of cells in series. For example, a 48V LiFePO4 battery typically has a nominal voltage of 51.2V (16 cells × 3.2V).
Nominal Capacity
Nominal capacity indicates the amount of charge a battery can store and deliver under standard test conditions, typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah). It defines how long a battery can supply a certain current before depletion. For instance, a 100Ah battery can theoretically provide 1A of current for 100 hours or 10A for 10 hours.
2. Why Are Nominal Voltage and Nominal Capacity Important?
Nominal values provide a reference for battery selection and performance comparison. They allow users to:
- Estimate runtime for specific applications.
- Compare batteries of different chemistries and configurations.
- Ensure compatibility with electrical systems.
- Predict charging and discharging behavior in practical applications.
3. Other Voltage and Capacity Terms
Beyond nominal voltage and capacity, several other key parameters define battery performance:
-
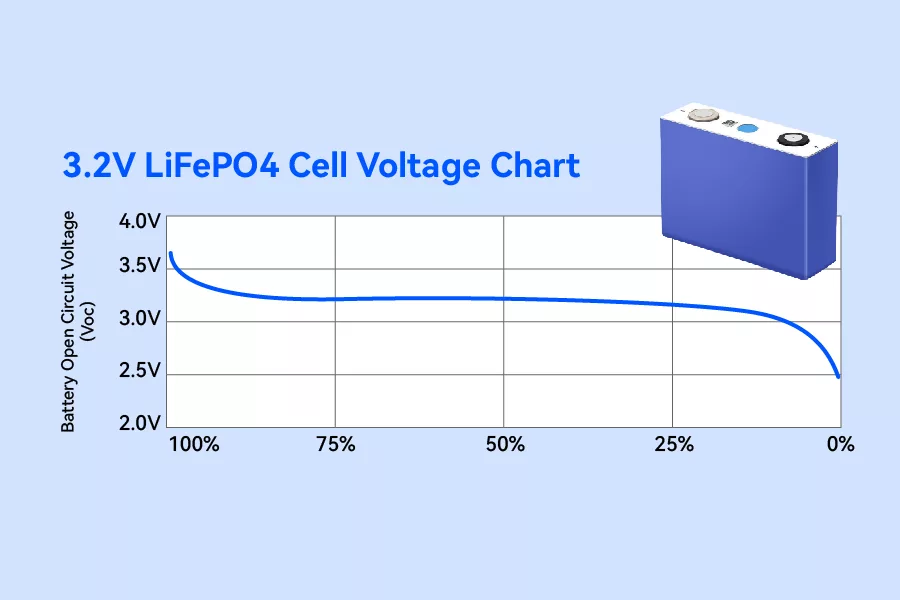
Operating Voltage (Working Voltage): The actual voltage range during operation, which depends on the battery’s charge level, load, and battery management system (BMS) settings.
- Example: A 48V LiFePO4 battery may have an operating voltage range of 43.2V to 58.4V, depending on brand-specific BMS configurations.
-
Charging Voltage: The voltage required to fully charge the battery. For LiFePO4 cells, this is typically 3.6V per cell, meaning a 48V pack (16 cells) requires a maximum charging voltage of 57.6V to 58.4V.
-
Discharge Cutoff Voltage: The lowest voltage at which the battery is considered discharged. For LiFePO4 cells, this is typically 2.5V per cell, making a 48V pack’s cutoff voltage around 40V to 43.2V, depending on BMS settings.
-
Nominal Current: The typical current draw for normal operation, impacting battery longevity and efficiency.
-
Internal Resistance: The inherent resistance within the battery that affects efficiency, heat generation, and performance. Lower resistance leads to better efficiency and less heat.
4. Common Terminology in Battery Specifications
Manufacturers use different terms to describe battery characteristics, including:
- Electrical Performance Parameters – Covers all key electrical specifications.
- Electrical Specifications – Defines voltage, capacity, current ratings, and other operational details.
- Battery Parameters – Focuses on technical indicators specific to batteries.
- Electrical Characteristics – Highlights core electrical properties.
- Rated Parameters – Specifies standard values under controlled conditions.
5. Example: 48V LiFePO4 Battery for Golf Carts
A 48V LiFePO4 battery used in golf carts typically has:
- Nominal voltage: 51.2V
- Operating voltage range: 43.2V – 58.4V (varies by BMS settings)
- Charging voltage: ~58.4V
- Cutoff voltage: ~43.2V
This provides a stable power supply with long-lasting performance, making it ideal for golf carts that require consistent energy output over extended use.
Understanding nominal voltage and nominal capacity, along with other key battery parameters, is essential for selecting and using batteries effectively. These specifications help ensure compatibility with different applications, optimize performance, and prolong battery lifespan. By considering these factors, users can make informed decisions when choosing batteries for electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and other power applications.

