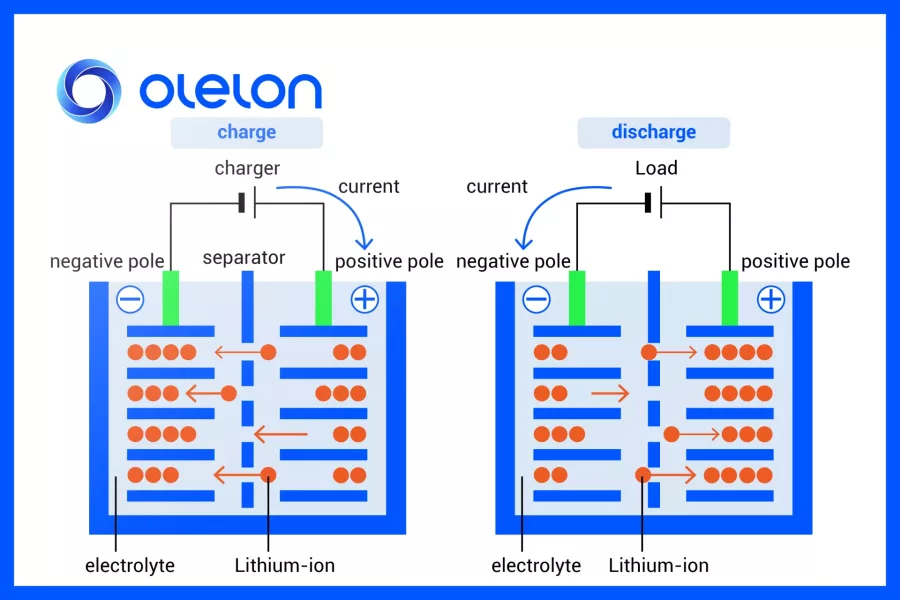
1. Chemistry and Structure of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries consist of a cathode (commonly lithium metal oxides such as LiCoO2, LiFePO4), an anode (graphite or other carbon materials), an electrolyte (lithium salts dissolved in an organic solvent), and a separator. During charge and discharge, lithium ions move between the cathode and anode, enabling energy storage and release.
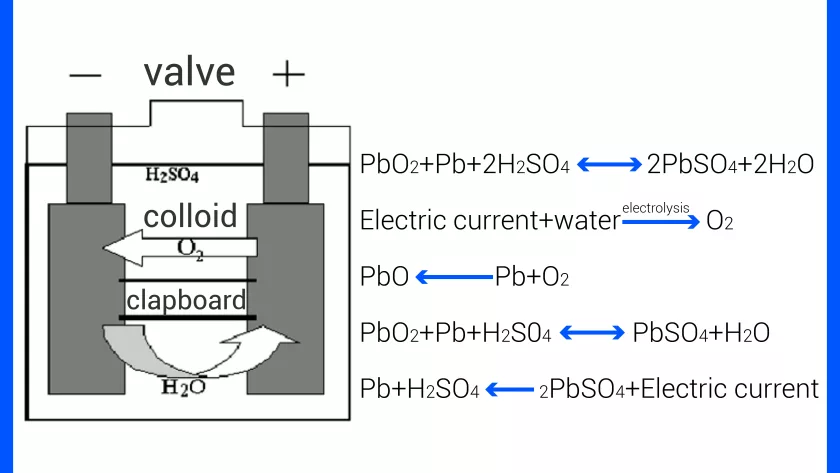
2. Chemistry and Structure of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries consist of a cathode (PbO2), an anode (spongy lead Pb), an electrolyte (diluted sulfuric acid H2SO4), and a separator. During discharge, PbO2 at the cathode and Pb at the anode undergo chemical reactions to form lead sulfate (PbSO4), while H+ and SO4^2- ions participate in the reaction. Charging reverses this reaction, restoring the original state.
3. Comparison Table
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Lead-Acid Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High (150-250 Wh/kg) | Low (30-50 Wh/kg) |
| Cycle Life | Long (2000-5000 cycles) | Short (300-800 cycles) |
| Discharge Rate | High, supports high power applications | Low, deep discharge affects lifespan |
| Discharge Voltage | Stable (3.2V for LiFePO4, 3.7V for Li-ion) | Fluctuates, typically 2V per cell |
| Charging Efficiency | High, fast charging with CC-CV mode | Low, potential overcharging issues |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Sensitive, poor low-temperature performance (optimized in some models) | Better low-temperature performance, but electrolyte evaporation at high temperatures |
| Applications | EVs, high-end energy storage, electronics, drones | Automotive starter batteries, backup power, UPS systems |
| Maintenance | Virtually maintenance-free, avoid overcharging | Requires electrolyte replenishment, avoid deep discharge |
Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, longer lifespan, and more efficient charging, making them the preferred choice for modern applications. However, lead-acid batteries still hold a market share in cost-sensitive areas. As lithium battery technology advances, its adoption is expected to expand further.